Azure Purview was introduced in Chapter 1. Azure Purview is very useful for governance, data discovery, and exploration. Keeping tabs on the data sources you have and what they contain is key to being able to securely manage them. There will be more on this in Chapter 8, which discusses data security and governance. When you click the Purview link, you are prompted to create an Azure Purview account or connect to one that you already have. You will do this later, at a more appropriate time.
Integration
The Triggers and the Integrated runtime features are directly related to pipelines, which is discussed in the section “Integrate,” which covers the features available when you select the Integrate hub option (refer to Figure 3.27).
You need a few things to make a pipeline work: something to trigger (invoke/execute) the pipeline and some compute to process the pipeline activity. Both of those needs are found in the Integration section on the Manage hub.
TRIGGERS
There are two ways to trigger a pipeline. You can do it manually, or you can schedule it. To manually trigger the pipeline in the Azure Synapse Analytics Studio (shown later), you can use REST API or Azure PowerShell. If you need the pipeline to run at scheduled intervals, for example, every hour, click the Triggers menu item followed by + New. If you have a Copy activity in your pipeline that ingests data from an ADLS container each hour, then you would want to schedule that here. Figure 3.36 shows an example of how that scheduled trigger configuration might look.
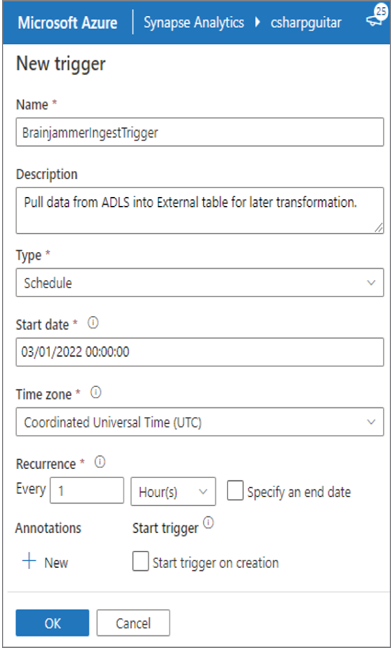
FIGUER 3.36 Azure Synapse Analytics integration triggers
There are four different types of triggers:
- Schedule triggers
- Tumbling window triggers
- Storage event triggers
- Custom event triggers
A tumbling window trigger has a few advantages over a scheduled trigger. For example, when you use a tumbling window trigger, you can run scheduled pipelines for past dates. This is not possible with scheduled triggers, which can only be run currently or at a future time. Failed pipeline runs triggered by a tumbling window trigger will be retried, whereas scheduled will not. Finally, tumbling window triggers can be bound only to a single pipeline, while a single scheduled trigger can invoke multiple pipelines, or multiple pipelines can be invoked by a single scheduled trigger. The storage event trigger is invoked when a blob is either created or deleted in the configured Azure Storage container. A custom event trigger provides the interface to subscribe to an Event Grid topic. An Event Grid is a product that acts as a middle tier between a message producer or a message queue and subscribers who want to receive those messages.
